X-linked carrier test
The X-Linked Carrier test is a test specifically designed for women who want a pregnancy. The test is used to investigate genetic mutations passed from a mother to her children where they cause disease.
The genetic mutations studied are linked to the X chromosome and cause X-linked recessive hereditary diseases. X-linked recessive hereditary disease has a mutation in a gene on the X chromosome and mainly affects boys. Men have one X and one Y chromosome, (XY); therefore, if the X chromosome is inherited with a mutation in a gene, men don’t have another X chromosome to compensate for the mutation, and they may be affected by a disease.
On the other hand, women have two X chromosomes (XX); therefore, if one of the X chromosomes is inherited with a mutation in a gene, women can compensate for the mutation with the other X chromosome and be healthy carriers. Since it is unlikely that women have two mutated copies of the gene which causes the disease, men are more affected by X-linked recessive inherited illness than women.
X-linked recessive Hereditary Diseases
In boys: one copy of the mutated gene is sufficient to cause the disease.
In girls: two copies of the mutated gene are needed to cause the disease; it is more likely that the woman inherits only one copy of the mutated gene and becomes a healthy carrier.
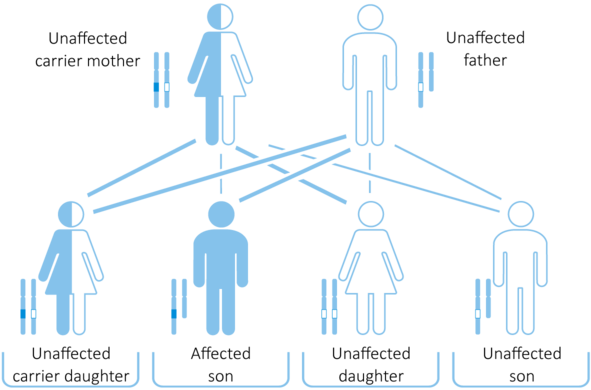
Timely counseling helps prevent X-linked disease such as:
- Adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD)
- Choroideremia
- Alport syndrome
- Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD)
- Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia
- Hemophilia A (HEMA)
- Hemophilia B (HEMB)
- Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy 6
- Fragile X syndrome
- Fabry disease
- Retinoschisis 1, X-linked, juvenile (RS1)
How to do it
